//
//MessageQueue.cpp
//Copyright (c) 2015 TOSHIYUKI ARAI. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
#include <oz++/Thread.h>
#include <oz++/MessageQueue.h>
namespace OZ {
class Writer :public Thread {
private:
MessageQueue queue;
public:
Writer(const char* qname)
:Thread()
{
queue.create(qname);
}
public:
void run()
{
int i = 0;
//You have to know the size of a message in your queue.
const long int size = queue.messageSize();
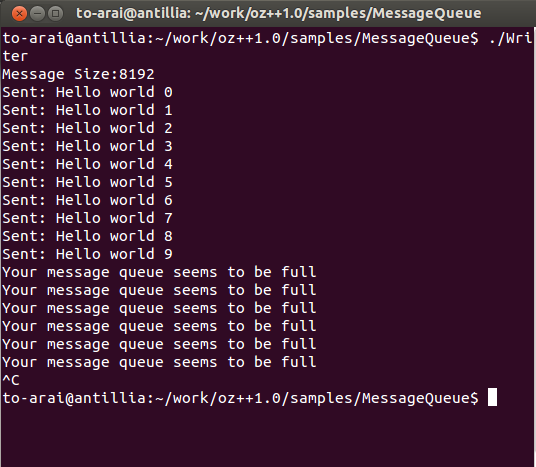
printf("Message Size:%ld\n", size); //Default size is 8192 bytes.
while(i < 100) {
if (queue.isWritable()) {
char message[size];
sprintf(message, "Hello world %d", i);
try {
//You may specify the real message size
// to the second argument of the send method of
// MessageQueue.
queue.send(message, strlen(message), 0);
printf("Sent: %s\n", message);
i++;
} catch (Exception& ex) {
caught(ex);
}
} else {
printf("Your message queue seems to be full\n");
sleep(1);
}
} //while
}
};
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
const char* qname = "/oz++_queue";
try {
Writer writer(qname);
writer.start();
writer.wait();
} catch (Exception& ex) {
caught(ex);
}
return 0;
}
|