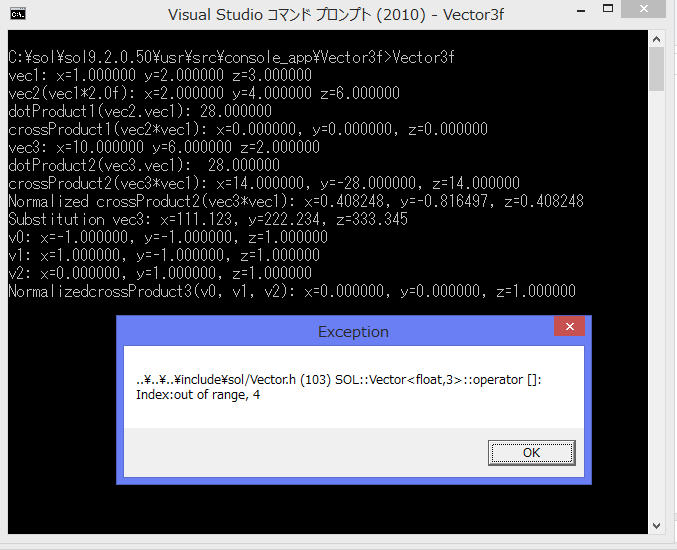
1 Screenshot
2 Source code
/*
* Vector3f.cpp
* Copyright (c) 2015 Antillia.com TOSHIYUKI ARAI. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
*/
#include <sol/Vector3f.h>
#include <sol/Vertex.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
try {
Vector3f vec1(1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f);
printf("vec1: x=%lf y=%lf z=%lf\n", vec1[0], vec1[1], vec1[2]);
Vector3f vec2(vec1);
vec2 *= 2.0f;
printf("vec2(vec1*2.0f): x=%lf y=%lf z=%lf\n", vec2[0], vec2[1], vec2[2]);
float dot = vec2.dotProduct(vec1);
printf("dotProduct1(vec2.vec1): %f\n", dot);
Vector3f cross = vec2.crossProduct(vec1);
printf("crossProduct1(vec2*vec1): x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n",
cross[0], cross[1], cross[2]);
Vector3f vec3(10.0f, 6.0f, 2.0f);
printf("vec3: x=%lf y=%lf z=%lf\n", vec3[0], vec3[1], vec3[2]);
float dot2 = vec3.dotProduct(vec1);
printf("dotProduct2(vec3.vec1): %f\n", dot2);
Vector3f cross2 = vec3.crossProduct(vec1);
printf("crossProduct2(vec3*vec1): x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n",
cross2[0], cross2[1], cross2[2]);
cross2.normalize();
printf("Normalized crossProduct2(vec3*vec1): x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n",
cross2[0], cross2[1], cross2[2]);
vec3[0] = 111.123f;
vec3[1] = 222.234f;
vec3[2] = 333.345f;
printf("Substitution vec3: x=%.3lf, y=%.3lf, z=%.3lf\n",
vec3[0], vec3[1], vec3[2]);
Vertex<3> triangle[] = {
//Face 1:
{-1.0,-1.0, 1.0 }, //0
{ 1.0,-1.0, 1.0 }, //1
{ 0.0, 1.0, 1.0 }, //2
};
Vector3f v0( triangle[0] );
Vector3f v1( triangle[1] );
Vector3f v2( triangle[2] );
printf("v0: x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n", v0[0], v0[1], v0[2]);
printf("v1: x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n", v1[0], v1[1], v1[2]);
printf("v2: x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n", v2[0], v2[1], v2[2]);
Vector3f n = Vector3f::crossProduct(v1 - v0, v2-v0);
n.normalize();
printf("NormalizedcrossProduct3(v0, v1, v2): x=%lf, y=%lf, z=%lf\n", n[0], n[1], n[2]);
vec3[4] = 444.456f; //Cause an exception
} catch (Exception& ex) {
ex.display();
}
return 0;
}
Last modified: 17 Aug 2016
Copyright (c) 2016 Antillia.com ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
