|
SOL4Py Class: ZCustomImageDataGenerator
|
We have created ZCustomImageDataGenerator class to augment images to use as the datasets for ML training or validation process by using Pillow image library
and ZSaultPepperNoiseInjector
For detail, please see the following source code.
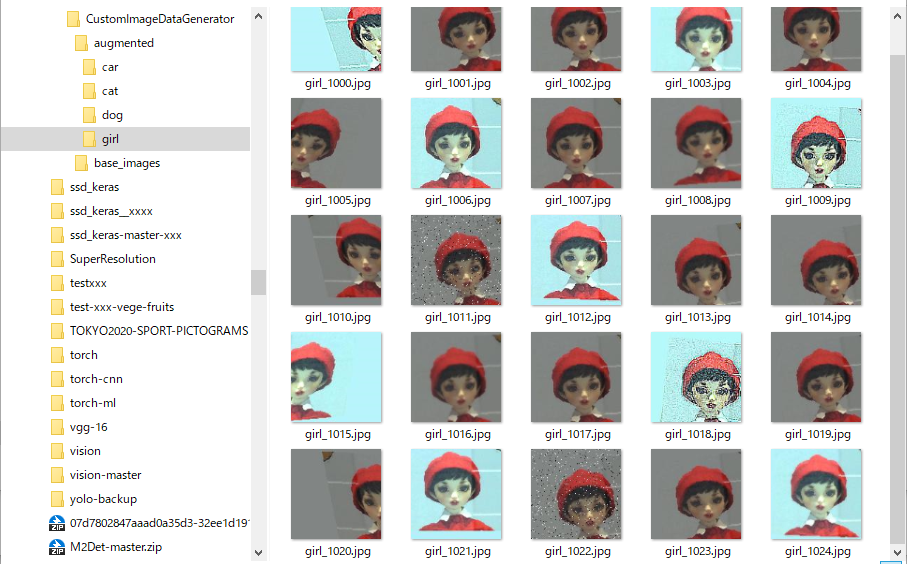
The following is a set of images generated by using the class in sample program CustomImageDataGenerator.
Source code
#/******************************************************************************
#
# Copyright (c) 2019 Antillia.com TOSHIYUKI ARAI. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
#
#******************************************************************************/
# 2019/07/10
# ZCustomImageDataGenerator.py
# See : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14177744/how-does-perspective-transformation-work-in-pil
# : https://programtalk.com/vs2/python/2533/maze-cv/CV/perspective.py/
# See also: https://github.com/aleju/imgaug
#
import os
import glob
from random import *
import numpy as np
from SOL4Py.ZSaultPepperNoiseInjector import *
from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageFilter
class ZCustomImageDataGenerator:
##
# Constructor
def __init__(self, rotation_angle=10, left_top_shift=(6, 6), shrink_ratio=(0.90, 0.90), background=None,
affine_shift_position=(0.25, 0.1), contrast=0.3, saultpepper_noise = 0.02, crop_size=128,
sharpening=True, smoothing=True, edge_enhancing=True, horizontal_flip=True, vertical_flip=False):
MAX_ANGLE=20
self.angle = rotation_angle # Rotation angle
# Limit rotation angle
if self.angle > MAX_ANGLE:
self.angle = MAX_ANGLE
self.x, self.y = left_top_shift # Relocation initial (x, y) position
# Limit left and top shift
MAX_SHIFT_X = 20
MAX_SHIFT_Y = 20
if self.x > MAX_SHIFT_X:
self.x = MAX_SHIFT_X
if self.y > MAX_SHIFT_Y:
self.y = MAX_SHIFT_Y
self.shrink_rw, self.shrink_rh = shrink_ratio # Shrink ratio
# Limiting maxmimum and minimum of shrinking_ratio
MAX_SRINK_RW = 0.99
MIN_SHRINK_RW= 0.7
MAX_SRINK_RH = 0.99
MIN_SHRINK_RH= 0.7
if self.shrink_rw > MAX_SRINK_RW:
self.shrink_rw = MAX_SRINK_RW
if self.shrink_rh > MAX_SRINK_RH:
self.shrink_rh = MAX_SRINK_RH
if self.shrink_rw < MIN_SHRINK_RW:
self.shrink_rw = MIN_SHRINK_RW
if self.shrink_rh < MIN_SHRINK_RH:
self.shrink_rh = MIN_SHRINK_RH
self.xshift, self.yshift = affine_shift_position # Shifting (x, y) position for AFFINE transformation
self.background = background
self.contrast = contrast # Constrast
self.noise = saultpepper_noise # Noise injection sault, pepper
self.crop_size = crop_size
self.sharpen = sharpening # Sharpening flag
self.smooth = smoothing # Smoothing flag
self.edge_enhance = edge_enhancing # Edge-enhancing flag
self.hflip = horizontal_flip # Horizontal flip flag
self.vflip = vertical_flip # Vertical flip flag
self.save = True # File save flag
# Create an object ZSaultPepperNoiseInjector
self.noise_injector = ZSaultPepperNoiseInjector(sault=self.noise, pepper=self.noise)
# Generate the number of count of augmented images from a source_image (PIL image)
def flow(self, source_image, n_augmentation=10):
square_size = min(source_image.size)
# Crop the source_image before a transformation.
self.preprocess(source_image, square_size)
self.width = source_image.width
self.height = source_image.height
# Background image size to paste the source_image
self.bwidth = self.width * 3
self.bheight = self.height * 3
print("Orginal image size {} {}".format(self.width, self.height))
# Get a bgcolor to fill background_image. For simplicity, we take one sampling point.
bgcolor = source_image.getpixel((4, 4))
if self.background != None:
bgcolor= self.background
# Create a PIL background image
background_image = Image.new("RGB", (self.bwidth, self.bheight), bgcolor)
for i in range(n_augmentation):
# Create a copy of source_image.
src_image = source_image.copy()
# Create a copy of background_image to paste a src_image
image = background_image.copy()
# (_px, _py): src_image pasting position in background_image
_px = (self.bwidth - self.width )/2
_py = (self.bheight - self.height)/2
# Paste the src_image to the background image.
image.paste(src_image, (int(_px), int(_py)))
# Transform the image
image = self.transform(i, image)
# Cropping the square region from the image(background_image).
cropped_image = self.postprocess(image, square_size)
yield cropped_image
# Generate the number of n_augmentation of augmented images from each image in image_folder
# and save them to save_folder if it is not None.
def flow_from_directory(self, image_folder, save_folder=None, save_format="jpg", n_augmentation=10):
files = glob.glob(image_folder) # image_folder = "./base_images/*/*.jpg" or ./base_images/*/*.png"
# save_folder = "./output/"
# Each image, say "foo_1001.jpg", augmented from an image file "foo.jpg" in a category folder "./base_images/category/"
# will be saved to save_folder as something like "./output/category/foo_1001.jpg"
for filename in files:
source_image = Image.open(filename)
square_size = min(source_image.size)
# Crop the source_image
source_image = self.preprocess(source_image, square_size)
self.width = source_image.width
self.height = source_image.height
# Background image size to paste the source_image
self.bwidth = self.width * 3
self.bheight = self.height * 3
# Get a bgcolor to fill background_image. For simplicity, we take only one sampling point.
bgcolor = source_image.getpixel((4, 4))
if self.background != None:
bgcolor= self.background
# Create a background image filled with self.background color (bgcolor).
background_image = Image.new("RGB", (self.bwidth, self.bheight), bgcolor)
category = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(filename))
print("category {}".format(category))
ftitle, fext = os.path.splitext(filename)
nameonly = os.path.basename(ftitle)
print("Orginal image size {} {}".format(self.width, self.height))
# Augment the source image.
for i in range(n_augmentation):
# Create a copy of source_image.
src_image = source_image.copy()
# Create a copy of the background_image to paste a src_image
image = background_image.copy()
# (_px, _py): src_image pasting position in background_image
_px = (self.bwidth - self.width )/2
_py = (self.bheight - self.height)/2
# Paste the src_image to the background image.
ch = len(src_image.getbands())
#print(src_image.getbands(), ch) => ('R', 'G', 'B', 'A') 4
if ch == 4:
image.paste(src_image, (int(_px), int(_py)), mask=src_image.split()[3])
else:
image.paste(src_image, (int(_px), int(_py)))
# Transform the image
image = self.transform(i, image)
# Cropping the square region from the image(background_image).
cropped_image = self.postprocess(image, square_size)
# If save_folder is specified, save the cropped_image to a file
if save_folder != None:
save_filename = nameonly + "_" + str(1000+i) + "." + save_format
out_folder = os.path.join(save_folder, category)
if not os.path.exists(out_folder):
os.makedirs(out_folder)
save_pathname = os.path.join(out_folder, save_filename)
# Save cropped_image to a file.
cropped_image.save(save_pathname)
print("Saved to " + save_pathname)
yield cropped_image
# Stage1: Preprocessing source_image prior to a transformation.
def preprocess(self, source_image, square_size):
cx = (source_image.width - square_size )/2
cy = (source_image.height - square_size )/2
crop_box = (cx, cy , cx + square_size, cy + square_size)
source_image = source_image.crop(crop_box)
MARGIN = 10
# Resize source_image by the rectangle of size (self.crop_size+MARGIN, self.crop_size+MARGIN)
if square_size > (self.crop_size+MARGIN):
source_image = source_image.resize(size=(self.crop_size+MARGIN, self.crop_size+MARGIN))
return source_image
# State2: Transformation an image by using some randomizations.
def transform(self, i, image):
# (_x, _y): random translation position
_x = np.random.randint(0, self.x)
_y = np.random.randint(0, self.y)
# _angle : random rotation angle
_angle = np.random.randint(0, self.angle)
minw = float(image.width) * float(self.shrink_rw)
minh = float(image.height)* float(self.shrink_rh)
# (_w, _h) : random image_width and image_height
self._w = int( np.random.randint(int(minw), image.width) )
self._h = int( np.random.randint(int(minh), image.height) )
print(" {} {} {} {}".format(_x, _y, self._w, self._h))
if i % 3 == 0:
_angle = _angle * (-1)
# Resize the image to (_w, _h)
image = image.resize(size=(self._w, self._h), resample=Image.LANCZOS)
# Rotate the image by _angle
image = image.rotate(_angle, translate=(_x, _y), expand=True)
if i % 3 == 0:
print("CONTRAST {}".format(i))
image = ImageOps.autocontrast(image, self.contrast)
if i % 4 == 0 and self.vflip == True:
print("VERTICAL FLIP {}".format(i))
image = ImageOps.flip(image)
if i % 5 == 0 and self.hflip == True:
print("HORIZONTAL FLIP {}".format(i))
image = ImageOps.mirror(image)
if i % 5 == 0:
# Apply a simple AFFINE transformation to the image.
xshift = int( abs(self.xshift) * self.width )
yshift = int( abs(self.yshift) * self.height )
# New width and height (_nw, _nh) for AFFINE transformation
_nw = self._w + xshift
_nh = self._h + yshift
# Very simple coefficients fo AFFINE transformation
coeffs = (1, self.xshift, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0)
# Inverting _xs flag.
self.xshift = self.xshift * (-1)
print("AFFINE {}".format(i))
image = image.transform((_nw, _nh), Image.AFFINE, coeffs, Image.BICUBIC)
if i % 6 == 0 and self.sharpen == True:
print("SHARPEN {}".format(i))
image = image.filter(ImageFilter.SHARPEN)
if i % 8 == 0 and self.smooth == True:
print("SMOOTH_MORE {}".format(i))
image = image.filter(ImageFilter.SMOOTH_MORE)
if i % 9 == 0 and self.edge_enhance == True:
print("EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE {}".format(i))
image = image.filter(ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE_MORE)
if i>0 and i % 11 == 0 and self.noise >0.0:
print("NOISE {}".format(i))
image = self.inject_saultpepper_noise(image)
return image
# Stage3: Postprocessing a tranformed image to crop an image after a transformation.
def postprocess(self, image, square_size):
square_size = max((self.bwidth, self.bheight))
# Cropping the square region from the image(background_image).
crop = square_size
if self.crop_size < square_size:
crop = self.crop_size
top = (self.bheight - crop)/2
bottom = top + crop
left = (self.bwidth - crop)/2
right = left + crop
box = (int(left), int(top), int(right), int(bottom))
cropped_image = image.crop(box)
return cropped_image
# Sault-Peper noise injection to a pil_image.
def inject_saultpepper_noise(self, pil_image):
arrayed_image = np.asarray(pil_image)
noised_image = self.noise_injector.inject_to(arrayed_image)
# Create a PIL image from the noised_image
return Image.fromarray(noised_image)
Last modified: 20 Sep. 2019
Copyright (c) 2019 Antillia.com ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
